Black Basta Ransomware: Why You Should Worry And How You Can Defend
What is Black Basta?
Black Basta is ransomware as a service (RaaS) that appeared in April 2022. There is, however, evidence that it has been developed since February. Black Basta operators employ a double extortion technique. That is, they encrypt files on targeted organizations’ systems and demand a ransom for decryption. In addition to encrypting files on targeted organizations’ systems and demanding ransom, they also maintain a dark web leak site. Here, they threaten to publish sensitive information if a ransom is not paid.
From the time Black Basta emerged, Black Basta affiliates were very active in deploying ransomware and extorting organizations. According to the information posted on the leak site, Black Basta affiliates have compromised over 75 organizations despite only being active for a few months.
The ransomware is written in C++ and affects both Windows and Linux systems. The ransomware encrypts users’ data with ChaCha20 and RSA-4096, and in order to speed up the encryption process, it encrypts 64-byte chunks with 128 bytes of unencrypted data between each region. During the encryption process, the faster ransomware is able to compromise systems, the more likely it is that defenses will be activated before the system is compromised. It is one of the key factors affiliates look for when joining a Ransomware-as-a-Service company.
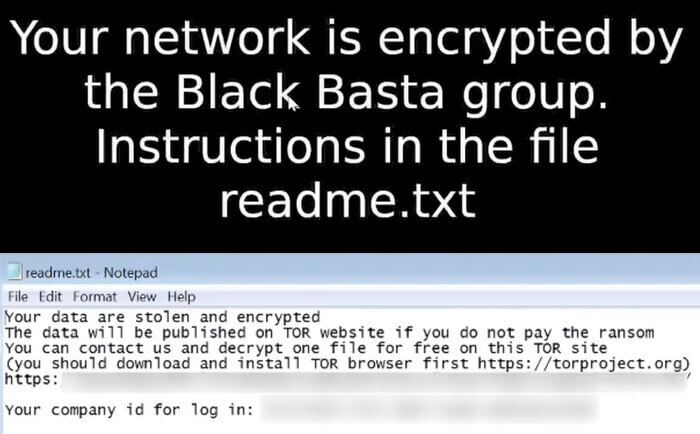
Black basta Ransom Background and Note
Blaack Basta Ransomware Blog – Victim List
Why is Black Basta so dangerous?
Besides the rapidly-growing victim list and the plethora of variants, Black Basta ransomware is notable for some other reasons. Among Black Basta’s victims are energy and utility companies across the globe and in the US.
In addition to versions that target Windows systems, VMWare ESXi variants of Black Basta have been discovered targeting Linux virtual machines as well.
Furthermore, many attacks have utilized Qakbot (also known as QBot) to spread throughout an organization, perform reconnaissance, steal data, and execute payloads.
The ransomware spawns a mutex with a string of dsajdhas.0 to ensure a single instance of the malware is running at a time. Then it will iterate through the entire file system, encrypting files with a file extension of .basta.
It writes the <random-charecters>.ico and <random-charecters>.jpg files to the %TEMP% directory. The .jpg file is leveraged to overwrite the desktop background to the ransom warning as shown in the aforementioned figure.
Additionally, a group policy object is created on compromised domain controllers to disable Windows Defender and anti-virus software.
Tactics, Techniques and Procedures
We have observed Black Basta affiliates leveraging the following TTPs:
| Tactic / Technique | Notes |
| TA0001 Initial Access | |
| T1566.001. Phishing: Spear phishing Attachment | Victims receive spear phishing emails with attached malicious zip files – typically password protected. That contains malicious doc including .doc, .pdf, .xls |
| TA0002 Execution | |
| T1569.002. System Services: Service Execution | Black Basta has installed and used PsExec to execute payloads on remote hosts. |
| T1047. Windows Management Instrumentation | Utilizes Invoke-TotalExec to push out the ransomware binary. |
| T1059.001. Command and Scripting Interpreter: PowerShell | Black Basta has encoded PowerShell scripts to download additional scripts. |
| TA0003 Persistence | |
| T1136. Create Account | Black Basta threat actors created accounts with names such as temp, r, or admin. |
| T1098. Account Manipulation | Added newly created accounts to the administrators’ group to maintain elevated access. |
| T1543.003. Create or Modify System Process: Windows Service | Creates benign-looking services for the ransomware binary. |
| T1574.001. Hijack Execution Flow: DLL Search Order Hijacking | Black Basta used Qakbot, which has the ability to exploit Windows 7 Calculator to execute malicious payloads. |
| TA0004 Privilege Escalation | |
| T1484.001. Domain Policy Modification: Group Policy Modification | Black Basta can modify group policy for privilege escalation and defense evasion. |
| T1574.001. Hijack Execution Flow: DLL Search Order Hijacking | Black Basta used Qakbot, which has the ability to exploit Windows 7 Calculator to execute malicious payloads. |
| T1543.003. Create or Modify System Process: Windows Service | Creates benign-looking services for the ransomware binary. |
| TA0005 Defense Evasion | |
| T1484.001. Domain Policy Modification: Group Policy Modification | Black Basta can modify group policy for privilege escalation and defense evasion. |
| T1218.010. System Binary Proxy Execution: Regsvr32 | Black Basta has used regsvr32.exe to execute a malicious DLL. |
| T1070.004. Indicator Removal on Host: File Deletion | Attempts to delete malicious batch files. |
| T1112. Modify Registry | Black Basta makes modifications to the Registry. |
| T1140. Deobfuscate/Decode Files or Information | Initial malicious .zip file bypasses some antivirus detection due to password protection. |
| T1562.001. Impair Defenses: Disable or Modify Tools | Disables Windows Defender with batch scripts, such as d.bat or defof.bat. |
| T1562.004. Impair Defenses: Disable or Modify System Firewall | Uses batch scripts, such as rdp.bat or SERVI.bat, to modify the firewall to allow remote administration and RDP. |
| T1562.009. Impair Defenses: Safe Boot Mode | Uses bcdedit to boot the device in safe mode. |
| T1574.001. Hijack Execution Flow: DLL Search Order Hijacking | Black Basta used Qakbot, which has the ability to exploit Windows 7 Calculator to execute malicious payloads. |
| T1622. Debugger Evasion | Uses IsDebuggerPresent to check if processes are being debugged. |
| TA0006 Credential Access | |
| T1555. Credentials from Password Stores | Black Basta uses Mimikatz to dump passwords. |
| TA0007 Discovery | |
| T1087.002. Account Discovery: Domain Account | Used commands such as net user /domain and net group /domain. |
| T1016. System Network Configuration Discovery | Lists internal IP addresses to target in C:\Windows\pc_list.txt – typically found on the Domain Controller. |
| T1082. System Information Discovery | Uses GetComputerName to query the computer name. |
| T1622. Debugger Evasion | Uses IsDebuggerPresent to check if processes are being debugged. |
| TA0008 Lateral Movement | |
| T1021.001. Remote Services: Remote Desktop Protocol | Black Basta has used RDP for lateral movement. |
| TA0009 Collection | |
| T1560.001. Archive Collected Data: Archive via Utility | |
| TA0010 Exfiltration | |
| T1567. Exfiltration over Web Service | |
| TA0011 Command and Control | |
| T1219. Remote Access Software | Black Basta has installed and used legitimate tools such as TeamViewer and AnyConnect on targeted systems. |
| T1573. Encrypted Channel | Uses Qakbot primarily and Cobalt Strike. |
| TA0040 Impact | |
| T1486. Data Encrypted for Impact | Black Basta modifies the Desktop background by adding a .jpg in C:\Temp and creating a registry key HKCU\Control Panel\Desktop. Additionally modifies the registry to change the icon of encrypted files.
It encrypts files excluding those with a .exe, .cmd, .bat and .com extension. Uses ChaCha20 or RSA-4096 to encrypt victims. |
| T1489. Service Stop | Uses sc stop and taskkill to stop services. |
| T1490. Inhibit System Recovery | Black Basta deletes Volume Shadow Copies using vssadmin. |
Table 1. Tactics, techniques and procedures for Black Basta activity.
How to Stay Protected from Black Basta Ransomware?
There are several ways that individuals and organizations can protect themselves against Black Basta and other types of ransomware. One of the most effective ways is to take regularly back up important data to an external hard drive or cloud-based storage service. This way, if the data is encrypted or lost due to ransomware, it can be restored from the backup. Other protective measures include deploying state-of-art endpoint protection software like ThreatResponder.
NetSecurity’s ThreatResponder, with its diverse capabilities, can help your team detect the most advanced cyber threats, including APTs, zero-day attacks, and ransomware attacks.
It can also help automate incident response actions across millions of endpoints, making it easy, fast, and hassle-free.
Want to try our ThreatResponder, cutting-edge Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR), and ThreatResponder FORENSICS, the Swiss knife for forensic investigators in action? Click on the below button to request a free demo of our NetSecurity’s ThreatResponder platform.
Indicators of compromise (IOCs)
| SHA256 | Detection |
| 5d2204f3a20e163120f52a2e3595db19890050b2faa96c6cba6b094b0a52b0aa | Ransom.Win32.BASTACRYPT.THDBGBB |
| 7883f01096db9bcf090c2317749b6873036c27ba92451b212b8645770e1f0b8a | Ransom.Win32.BASTACRYPT.YXCD2 |
| ae7c868713e1d02b4db60128c651eb1e3f6a33c02544cc4cb57c3aa6c6581b6e | Ransom.Win32.BASTACRYPT.THDBIBB |
| 17205c43189c22dfcb278f5cc45c2562f622b0b6280dcd43cc1d3c274095eb90 | Ransom.Win32.BASTACRYPT.YXCD2 |
| a54fef5fe2af58f5bd75c3af44f1fba22b721f34406c5963b19c5376ab278cd1 | Ransom.Win32.BASTACRYPT.THDBGBB |
| 1d040540c3c2ed8f73e04c578e7fb96d0b47d858bbb67e9b39ec2f4674b04250 | Ransom.Win32.BASTACRYPT.YXCD2 |
| 2967e1d97d32605fc5ace49a10828800fbbefcc1e010f6004a9c88ef3ecdad88 | Ransom.Win32.BASTACRYPT.YXCD2.note |
| f088e6944b2632bb7c93fa3c7ba1707914c05c00f9491e033f78a709d65d7cff | Ransom.Win32.BASTACRYPT.YXCD2.note |
For QAKBOT-related samples:
| SHA256 | Detections |
| a48ac26aa9cdd3bc7f219a84f49201a58d545fcebf0646ae1d676c7e43c6ac3e | TrojanSpy.Win32.QAKBOT.YACEDT |
| 82c73538322c8b90c25a99a7afc2fafcd7e7e03fe920a3331ef0003300ac10b8 | TrojanSpy.Win32.QAKBOT.YACEDT |
| 82c73538322c8b90c25a99a7afc2fafcd7e7e03fe920a3331ef0003300ac10b8 | TrojanSpy.Win32.QAKBOT.YACEDT |
| 2083e4c80ade0ac39365365d55b243dbac2a1b5c3a700aad383c110db073f2d9 | TrojanSpy.Win32.QAKBOT.YACEDT |
| 2e890fd02c3e0d85d69c698853494c1bab381c38d5272baa2a3c2bc0387684c1 | TrojanSpy.Win32.QAKBOT.YACEDT |
| 2d906ed670b24ebc3f6c54e7be5a32096058388886737b1541d793ff5d134ccb | TrojanSpy.Win32.QAKBOT.YACEDT |
| 72fde47d3895b134784b19d664897b36ea6b9b8e19a602a0aaff5183c4ec7d24 | TrojanSpy.Win32.QAKBOT.YACEDT |
| ffa7f0e7a2bb0edf4b7785b99aa39c96d1fe891eb6f89a65d76a57ff04ef17ab | TrojanSpy.Win32.QAKBOT.YACEDT |
| 1e7174f3d815c12562c5c1978af6abbf2d81df16a8724d2a1cf596065f3f15a2 | TrojanSpy.Win32.QAKBOT.YACEDT |
| 130af6a91aa9ecbf70456a0bee87f947bf4ddc2d2775459e3feac563007e1aed | Trojan.Win64.QUAKNIGHTMARE.YACEJT |
| 81a6c44682b981172cd85ee4a150ac49f838a65c3a0ed822cb07a1c19dab4af5 | Ransom.Win32.BASTACRYPT.YACEDT |
| 94428d7620fff816cb3f65595978c6abb812589861c38052d30fa3c566e32256 | Ransom.Win32.BASTACRYPT.YACEDT |
| c9df12fbfcae3ac0894c1234e376945bc8268acdc20de72c8dd16bf1fab6bb70 | Ransom.Win32.BASTACRYPT.YACEJT |
| 0d3af630c03350935a902d0cce4dc64c5cfff8012b2ffc2f4ce5040fdec524ed | Trojan.Win32.BLACKBASTA.YXCEJ |
| 3fe73707c2042fefe56d0f277a3c91b5c943393cf42c2a4c683867d6866116fc | Trojan.Win32.BLACKBASTA.YXCEJ |
| 3fe73707c2042fefe56d0f277a3c91b5c943393cf42c2a4c683867d6866116fc | Trojan.Win32.BLACKBASTA.YXCEJ |
| 0e2b951ae07183c44416ff6fa8d7b8924348701efa75dd3cb14c708537471d27 | Trojan.Win32.BLACKBASTA.YXCEJ |
| 8882186bace198be59147bcabae6643d2a7a490ad08298a4428a8e64e24907ad | Trojan.Win32.BLACKBASTA.YXCEJ |
| df35b45ed34eaca32cda6089acbfe638d2d1a3593d74019b6717afed90dbd5f8 | Trojan.Win32.BLACKBASTA.YXCEJ |
| b8aa8abac2933471e4e6d91cb23e4b2b5a577a3bb9e7b88f95a4ddc91e22b2cb | TrojanSpy.VBS.KEYLOAD.A |
| fb3340d734c50ce77a9f463121cd3b7f70203493aa9aff304a19a8de83a2d3c9 | TrojanSpy.VBS.KEYLOAD.A |
| 5ab605b1047e098638d36a5976b00379353d84bd7e330f5778ebb71719c36878 | TrojanSpy.VBS.KEYLOAD.A |
| 9707067b4f53caf43df5759fe40e9121f832e24da5fe5236256ad0e258277d88 | TrojanSpy.VBS.KEYLOAD.A |
| 9707067b4f53caf43df5759fe40e9121f832e24da5fe5236256ad0e258277d88 | TrojanSpy.VBS.KEYLOAD.A |
| d7580fd8cc7243b7e16fd97b7c5dea2d54bcba08c298dc2d82613bdc2bd0b4bf | TrojanSpy.VBS.KEYLOAD.A |
| 919d1e712f4b343856cb920e4d6f5d20a7ac18d7386673ded6968c945017f5fd | TrojanSpy.VBS.KEYLOAD.A |
| 012826db8d41ff4d28e3f312c1e6256f0647bf34249a5a6de7ecac452d32d917 | TrojanSpy.VBS.KEYLOAD.A |
| d36a9f3005c5c24649f80722e43535e57fd96729e827cdd2c080d17c6a53a893 | TrojanSpy.VBS.KEYLOAD.A |
| 580ce8b7f5a373d5d7fbfbfef5204d18b8f9407b0c2cbf3bcae808f4d642076a | Backdoor.Win32.COROXY.YACEKT |
Disclaimer
The page’s content shall be deemed proprietary and privileged information of NETSECURITY CORPORATION. It shall be noted that NETSECURITY CORPORATION copyrights the contents of this page. Any violation/misuse/unauthorized use of this content “as is” or “modified” shall be considered illegal and subjected to articles and provisions that have been stipulated in the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and Personal Data Protection Law (PDPL).











